Carbon and alloy steel for the production of screws and bolt Non-stainless
Non-stainless screws compliant with the standard EN ISO 898-1:2013 are subdivided into resistance classes and identified by a symbol consisting of two numbers: the first represents the hundredth part of the nominal value of the tensile strength (Rm) expressed in MPa, while the second represents the ratio between the yield strength ReL (or the specific characteristic proof stress Rp0.2) and the tensile strength Rm multiplied by ten.Reference is made to the European standard in this section. The steels listed in the section “American steels compliant with the ASTM standards” must be used for the production of screws and bolts according to the ASTM standards.
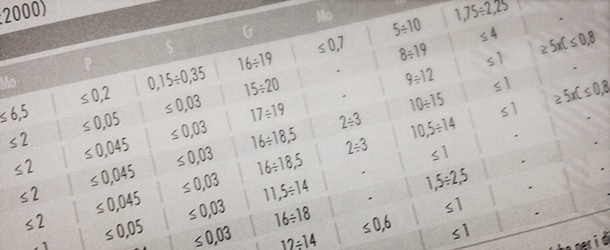
Chemical composition (%) (EN ISO 898-1:2013)
| Strength class | Material and heat treatment | Chemical composition (analysis on the product) % | Minimum hardening temperature °C | ||||
| C | P | S | B | ||||
| min | max | max | max | max | |||
| 4.6(1) | Carbon steel | - | 0,55 | 0,050 | 0,060 | Not specified | - |
| 4.8(1) | 0,13 | 0,55 | 0,050 | 0,060 | |||
| 5.6 | - | 0,55 | 0,050 | 0,060 | |||
| 5.8(1) | |||||||
| 6.8(1) | 0,15 | 0,55 | 0,050 | 0,060 | |||
| 8.8(2)(3) | Carbon or alloy steel (B, Mn, Cr), quenched and tempered | 0,15(3) | 0,40 | 0,025 | 0,025 | 0,003 | 425 |
| Quenched and tempered carbon steel | 0,25 | 0,55 | 0,025 | 0,025 | |||
| Quenched and tempered alloy steel | 0,20 | 0,55 | 0,025 | 0,025 | |||
| 9.8(2)(3) | Carbon or alloy steel (B, Mn, Cr), quenched and tempered | 0,15(3) | 0,40 | 0,025 | 0,025 | 0.003 | 425 |
| Quenched and tempered carbon steel | 0,25 | 0,55 | 0,025 | 0,025 | |||
| Quenched and tempered alloy steel | 0,20 | 0,55 | 0,025 | 0,025 | |||
| 10.9(3) | Carbon or alloy steel (B, Mn, Cr), quenched and tempered | 0,20(3) | 0,55 | 0,025 | 0,025 | 0,003 | 425 |
| Quenched and tempered carbon steel | 0,25 | 0,55 | 0,025 | 0,025 | |||
| Quenched and tempered alloy steel | 0,20 | 0,55 | 0,025 | 0,025 | |||
| 12.9(4) | Quenched and tempered alloy steel | 0,30 | 0,50 | 0,025 | 0,025 | 0,003 | 425 |
| 12.9(4) | Quenched and tempered carbon steel with the addition of Cr, B, Mn, Mo | 0,28 | 0,50 | 0,025 | 0,025 | 0,003 | 380 |
(1) For these classes it is possible to use free-cutting steel with maximum values of S=0.34%, P=0.11%, Pb=0.35%
(2) In order to obtain sufficient temperability with the nominal diameters >20 mm, it may be necessary to use steels of the 10.9 class
(3) In the case of carbon steels alloyed with boron with C < 0.25, the manganese must be ≥ 0.6% for the strength class 8.8 and ≥ 0.7% for the strength classes 9.8 and 10.9
(4) The class 12.9 differs from 10.9 for the different minimum hardening temperature
Mechanical characteristics (EN ISO 898-1:2013)
| Characteristics | Strength class | |||||||||||
| 4.6 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 5.8 | 6.8 | 8.8 d≤16mm | 8.8 d>16mm | 9.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 | |||
| Tensile strength Rm (MPa) | nom | 400 | 400 | 500 | 500 | 600 | 800 | 800 | 900 | 1000 | 1200 | |
| min | 400 | 420 | 500 | 520 | 600 | 800 | 830 | 900 | 1040 | 1220 | ||
| Yield strength Rm (MPa) ReL up to 6.8 - Rp0,2 from 8.8 | nom | 240 | - | 300 | - | - | 640 | 640 | 720 | 900 | 1080 | |
| min | 240 | - | 300 | - | - | 640 | 660 | 720 | 940 | 1100 | ||
| Elongation after fracture, a% | min | 22 | - | 20 | - | - | 12 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 8 | |
| Necking Z% | 52 | 52 | 48 | 48 | 44 | |||||||
| Vickers hardness (HV) F ≥ 98 N | min | 120 | 130 | 155 | 160 | 190 | 250 | 255 | 290 | 320 | 385 | |
| max | 220 | 220 | 220 | 220 | 250 | 320 | 335 | 360 | 380 | 435 | ||
| Brinell hardness (HB) F = 30D2 | min | 114 | 124 | 147 | 152 | 181 | 238 | 242 | 276 | 304 | 314 | |
| max | 209 | 209 | 209 | 209 | 238 | 304 | 318 | 342 | 361 | 414 | ||
| Rockwell hardness HRB up to 6.8 - HRC from 8.8 | min | 67 | 71 | 79 | 82 | 89 | 22 | 23 | 28 | 32 | 39 | |
| max | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 99,5 | 32 | 34 | 37 | 39 | 44 | ||
| Resilience KV (J) – 20°C(1) | min | - | - | 27 | - | - | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
(1) Applicable for diameters ≥ 16 mm
Examples of usable materials
As an example, some materials commonly used for the production of screws according to different production processes are provided, with reference to the standard EN ISO 898-1:2013. The mechanical characteristics depend on the type of screw produced and on the way it which it was made. The examples reported regard the European standard ISO 898-1:99.
| Strength classes | Production methods | Thread diameter | Examples of material used |
| 4.6 | Chip removal | ≤39 | 11SMn30 - Led108 - Telby - AVZ(1) - PS113(1) - TelbyPlus (1) - Telyx(1) |
| Cold deformation | ≤39 | SB4 – CB10FFS | |
| 4.8 | Chip removal | ≤39 | 11SMn30 - Led108 - Telby - AVZ(1) - PS113(1) - TelbyPlus (1) - Telyx(1) |
| Cold deformation | ≤39 | SB4 – CB10FFS | |
| 5.6 | Chip removal | ≤15 | SB4 |
| Cold deformation | ≤39 | CB10FFS | |
| 5.8 | Chip removal | ≤30 | 11SMn30 - Led108 - Telby - AVZ(1) - PS113(1) - TelbyPlus (1) - Telyx(1) |
| Cold deformation | ≤15 | SB4 | |
| ≤39 | C20 - CB10FFS | ||
| 6.8 | Chip removal | ≤16 | PR60 |
| ≤39 | PR80 – PR38 – 35S20 – 45S20 | ||
| Cold deformation | ≤13 | CB 10 FF S(2) - C20(2) | |
| 8.8 | Chip removal | ≤26 | 34CrS4 |
| ≤39 | RK1 Pb(1) C40 Pb(2) | ||
| Cold deformation | ≤26 | 34Cr4 | |
| ≤32 | Rk1 - RD6 - RK4 - 37CrS4 - 51CrV4 | ||
| 9.8 | Chip removal | ≤16 | 34CrS4 - 37CrS4 |
| Cold deformation | ≤16 | 34CrS4 - 37CrS4 | |
| 10.9 | Chip removal | ≤22 | 34CrS4 - 37CrS4 |
| ≤39 | RK1 Pb(1) | ||
| Cold deformation | ≤22 | 34Cr4 - 37CrS4 | |
| ≤27 | RD6 - RK4 - 37CrS4 | ||
| ≤39 | RK1 – RB2 - 51CrV4 - 34CrNiMo6 | ||
| 12.9 | Chip removal | ≤28 | RK1 - 51CrV4 |
| ≤30 | RB2 | ||
| Cold deformation | ≤28 | RK1 - 51CrV4 | |
| ≤30 | RB2 - 34CrNiMo6 |
(1) Materials that, while not completely satisfying the standard, are frequently used upon agreement between the producer and user of the screws
(2) Materials that can only satisfy the characteristics in the drawn state








